Shorten curing time

Curing involves any process used to initiate or catalyze structural changes at the chemical or molecular level in polymeric materials such as epoxies, phenolics, polyesters, and silicones. These materials are applied to a variety of products for bonding, protecting coatings, sealing, and insulating.
IH is typically used to heat metals and other conductive materials, but plastics and other non-conductive materials can also be heated by using conductive metals as susceptors for heat conduction. The power range of RF power supplies for typical curing applications is approximately 1 to 5 kW, depending on the material to be heated and requirements.
Video: IH curing application examples
Advantages of IH
- Energy savings: energy is supplied only to the susceptor plate, minimizing waste heat
- Improved working environment: occupants are not exposed to hot rooms, reducing the need for air conditioning
- Improved safety: Lower overall process temperatures and eliminate fire hazards
- Improved production rates: Induction heating is integrated into the production line
Curing epoxy
Adhesive curing for bonding metal parts using induction heating is used in many automotive manufacturing processes, including the assembly of clutch plates, brake shoes, and bumper parts. Shafts are typically bonded to cage rotors in the manufacture of small motors.
In copy machines, plastic parts are glued to aluminum rotors. This is an application where a foam roller is fixed to a metal shaft with a thermoplastic adhesive, and when the roller wears out, the shaft is heated and the foam roller is replaced.
Adhesion of filter assemblies
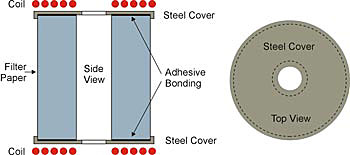
Filter assemblies are produced by curing thermosetting material between a steel or aluminum cover and filter paper. As shown in the figure above, two pancake-shaped induction coils are used to heat the top and bottom. When the object to be heated is moving, a longer pancake-shaped coil is used.
Partially heat at 150-175°C to ensure that the filter does not damage itself and has sufficient adhesion when cooled. Heat cycle is about 5-10 seconds.